Key Takeaways
- Mitochondria produce 90% of your body’s energy through ATP production, making them essential for sustained vitality
- Caffeine provides temporary stimulation but doesn’t address cellular energy deficiency at the mitochondrial level
- Liquid mitochondrial support formulas offer 3-5x faster absorption compared to capsules, delivering nutrients directly to cells
- Natural ATP boosters like CoQ10, PQQ, and B-vitamins support mitochondrial biogenesis and cellular metabolism
- Recognizing mitochondrial dysfunction symptoms early can help you address energy problems at their source

Introduction: The Real Source of Your Energy Crisis
We’ve been conditioned to believe that fatigue requires caffeine. Feeling sluggish at 2 PM? Grab another coffee. Can’t focus during your afternoon meeting? Energy drink to the rescue. But what if this approach is merely masking a deeper problem—one that exists at the cellular level, in the microscopic powerhouses called mitochondria?
Every cell in your body contains these tiny organelles working tirelessly to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecular currency of energy. When your mitochondria aren’t functioning optimally, no amount of caffeine can truly solve the problem. You’re essentially whipping tired horses rather than feeding them properly. The result? A cycle of stimulation followed by crashes, oxidative stress accumulation, and progressively declining cellular metabolism[1].
This comprehensive guide explores how bioavailable mitochondrial support through liquid supplementation offers a scientifically-backed alternative to caffeine dependency. You’ll discover the mechanisms behind true cellular energy production, recognize the signs of mitochondrial dysfunction, and learn why liquid delivery systems represent a paradigm shift in how we nourish our cells. By the end, you’ll understand how to support your body’s natural energy production at the most fundamental level—giving your mitochondria exactly what they need to keep you energized throughout the day.
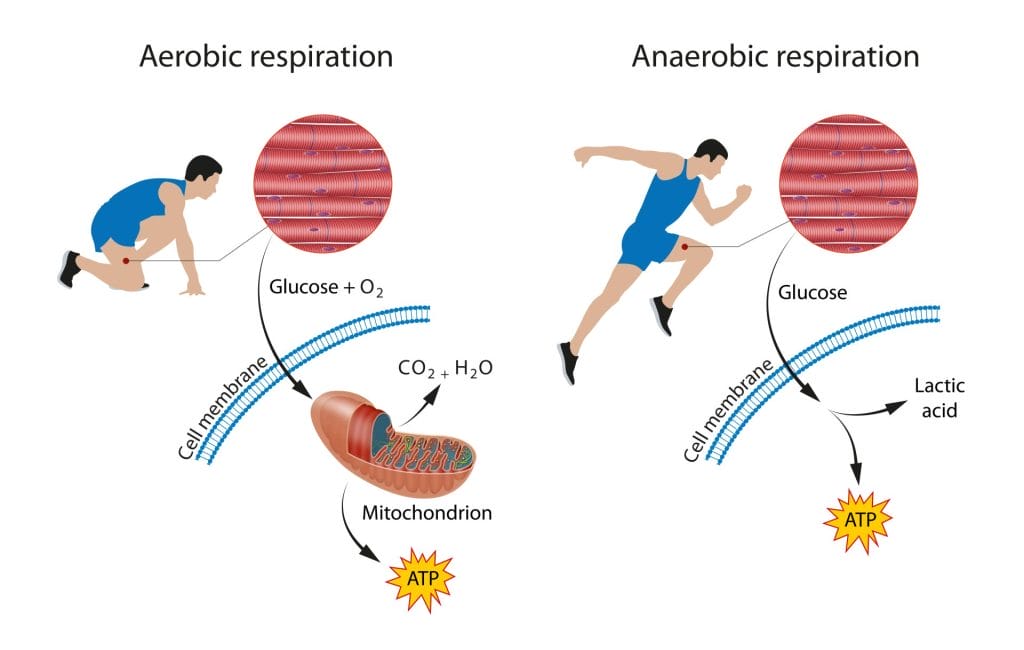
Understanding Your Cellular Power Plants: Mitochondria 101
What Are Mitochondria and Why Do They Matter?
Mitochondria are double-membraned organelles found in nearly every cell of your body, with some cells containing thousands of these energy factories. Often called the “powerhouses of the cell,” mitochondria convert nutrients from food into ATP through a complex process called oxidative phosphorylation[2]. This process is so efficient that a single glucose molecule can yield up to 38 ATP molecules when mitochondria are functioning optimally.
Your heart cells contain approximately 5,000 mitochondria per cell, while your liver cells may contain up to 2,000—reflecting the enormous energy demands these organs face[3]. When mitochondrial function declines, these high-demand tissues are typically the first to show symptoms, manifesting as cardiovascular issues, cognitive fog, and metabolic dysfunction.
The ATP Production Process: Your Body’s Energy Currency
ATP production occurs through three main stages:
- Glycolysis: Occurs in the cytoplasm, breaking down glucose into pyruvate
- Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Takes place in the mitochondrial matrix, generating electron carriers
- Electron Transport Chain: Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, produces the majority of ATP molecules
This intricate process requires specific cofactors and nutrients including CoQ10, B-vitamins, magnesium, and L-carnitine. When even one of these essential components is deficient, the entire energy production system becomes compromised[4]. This is where targeted mitochondrial support becomes crucial—not as a stimulant, but as fundamental cellular nutrition.
Mitochondrial Biogenesis: Creating New Energy Factories
One of the most exciting discoveries in cellular biology is mitochondrial biogenesis—your body’s ability to create new mitochondria. This process is regulated by proteins like PGC-1α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha) and can be stimulated through exercise, caloric restriction, and specific nutrients[5].

Supporting mitochondrial biogenesis means you’re not just optimizing existing mitochondria but actually increasing their numbers. Compounds like pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) have been shown to stimulate the production of new mitochondria, offering a pathway to genuinely enhanced cellular capacity rather than temporary stimulation[6].
Mitochondrial Dysfunction Symptoms: Is Your Cellular Energy Compromised?
Common Warning Signs of Mitochondrial Decline
Mitochondrial dysfunction affects approximately 1 in 4,000 people with genetic mitochondrial diseases, but far more individuals experience subclinical mitochondrial impairment due to aging, stress, poor nutrition, and environmental toxins[7]. Recognizing the symptoms early allows for intervention before serious health complications develop.

Key mitochondrial dysfunction symptoms include:
- Persistent fatigue: Exhaustion disproportionate to activity level, unrelieved by sleep
- Exercise intolerance: Rapid muscle fatigue, prolonged recovery times, post-exertional malaise
- Cognitive difficulties: Brain fog, poor concentration, memory problems
- Muscle weakness: Particularly in activities requiring sustained effort
- Neurological issues: Migraines, seizures, developmental delays in children
- Gastrointestinal problems: Chronic constipation, reflux, difficulty gaining weight
- Cardiovascular symptoms: Heart palpitations, abnormal heart rhythms
- Vision and hearing loss: Progressive sensory decline
The Aging-Mitochondria Connection
Mitochondrial function naturally declines with age, with some studies showing a 50% reduction in mitochondrial ATP production capacity by age 70[8]. This decline contributes to many age-related conditions including sarcopenia (muscle loss), cognitive decline, and reduced exercise capacity. The accumulation of oxidative stress and mitochondrial DNA mutations creates a downward spiral affecting overall vitality.

However, this decline isn’t inevitable or irreversible. Research demonstrates that targeted nutritional support can significantly improve mitochondrial function even in older adults, essentially “rejuvenating” cellular energy production[9]. Understanding age-related nutrient deficiencies becomes crucial for maintaining mitochondrial health throughout the lifespan.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Modern life presents unique challenges to mitochondrial health:
- Chronic stress: Elevates cortisol, increasing oxidative stress and depleting mitochondrial cofactors
- Poor diet: Processed foods lack essential nutrients while promoting inflammation
- Toxin exposure: Heavy metals, pesticides, and pollutants directly damage mitochondria
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of movement signals the body to reduce mitochondrial numbers
- Sleep deprivation: Impairs mitochondrial repair and regeneration processes
These factors create a perfect storm for mitochondrial dysfunction, making proactive cellular support more important than ever[10].

Sample blog
Glam Dust
Radiant Skin – Luscious Hair – Pristine Nails
Vitamin Shots
The Ultimate Brain And Body Supplement
Vitamin Sprinkles
Fuel Your Brain – Nourish Your Body – With One Delicious Sprinkle
Natural ATP Boosters: The Essential Nutrients Your Mitochondria Crave
Coenzyme Q10: The Electron Transport Chain Essential
CoQ10 serves as a critical electron carrier in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, directly participating in ATP production. This fat-soluble antioxidant also protects mitochondrial membranes from oxidative damage[11]. Your body produces CoQ10 naturally, but production declines significantly after age 30, and certain medications (particularly statins) further deplete levels.
Research shows that CoQ10 supplementation can improve energy levels, exercise performance, and cardiovascular function. A study of 50 patients with chronic fatigue found that 200mg daily of CoQ10 significantly improved fatigue scores and biochemical markers of mitochondrial function[12].
The form matters significantly: ubiquinol (the reduced form) offers superior bioavailability compared to ubiquinone, particularly for individuals over 40 whose ability to convert ubiquinone to ubiquinol is diminished.
PQQ: The Mitochondrial Biogenesis Stimulator
Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) represents a breakthrough in mitochondrial support. Unlike many nutrients that optimize existing mitochondria, PQQ actually stimulates the creation of new mitochondria through activation of cellular signaling pathways[13]. This compound also provides powerful antioxidant protection, being capable of catalyzing thousands of oxidation-reduction reactions before degradation.
Human studies have demonstrated that 20mg daily of PQQ can improve cognitive function, sleep quality, and subjective energy levels within just 8 weeks[14]. When combined with CoQ10, the effects are synergistic, providing both protection of existing mitochondria and generation of new ones.
B-Complex Vitamins: The Metabolic Cofactors
The B-vitamins serve as essential cofactors throughout the energy production process:
- B1 (Thiamine): Critical for pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, converting pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
- B2 (Riboflavin): Forms FAD, an electron carrier in the electron transport chain
- B3 (Niacin): Forms NAD+, essential for glycolysis and the Krebs cycle
- B5 (Pantothenic Acid): Component of Coenzyme A, vital for fatty acid metabolism
- B6 (Pyridoxine): Involved in amino acid metabolism and neurotransmitter synthesis
- B9 (Folate): Supports one-carbon metabolism and mitochondrial protein synthesis
- B12 (Cobalamin): Essential for mitochondrial fatty acid metabolism and myelin maintenance
Deficiency in any single B-vitamin can create bottlenecks in cellular metabolism, reducing ATP production capacity regardless of other factors[15]. Complete guide to B-complex vitamins provides deeper insights into these critical nutrients.
Additional Mitochondrial Support Nutrients
L-Carnitine: Transports fatty acids into mitochondria for beta-oxidation, particularly important for heart and skeletal muscle energy production. Acetyl-L-carnitine crosses the blood-brain barrier, supporting neuronal mitochondrial function[16].
Magnesium: Required for over 300 enzymatic reactions, including ATP synthesis. Magnesium actually binds to ATP to create the biologically active form (Mg-ATP). Deficiency directly impairs energy production at the most fundamental level.
Alpha-Lipoic Acid: A potent antioxidant that regenerates other antioxidants like CoQ10 and vitamins C and E. It also improves glucose metabolism and mitochondrial function, particularly beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance[17].
Liquid CoQ10 vs Capsules: The Bioavailability Revolution
Understanding Bioavailability and Absorption
Bioavailability refers to the proportion of a nutrient that enters circulation and reaches target tissues. With oral supplements, this is influenced by dissolution, absorption, first-pass metabolism, and tissue uptake. Many fat-soluble nutrients like CoQ10 have notoriously poor bioavailability in standard capsule form—often below 10%[18].
This means that a 100mg CoQ10 capsule might deliver only 10mg to your bloodstream, with even less reaching mitochondrial membranes where it’s actually needed. This bioavailability problem represents a massive inefficiency in supplementation, essentially wasting 90% of the product.
The Liquid Advantage: Speed and Efficiency
Liquid formulations fundamentally change this equation through several mechanisms:
1. Pre-dissolved nutrients: Liquid supplements bypass the dissolution phase entirely, immediately available for absorption. Capsules must first disintegrate and dissolve, processes that can take 30-60 minutes and are highly variable based on digestive capacity.
2. Enhanced absorption surface area: Liquids begin absorption in the mouth through the mucous membranes, providing an additional absorption pathway that bypasses first-pass liver metabolism[19].
3. Reduced digestive demands: Individuals with compromised digestion—whether from age, illness, or medications—often cannot effectively break down capsules or tablets. Liquid formulations eliminate this barrier.
4. Optimal delivery systems: Modern liquid formulations use liposomal technology, nanoemulsions, or micellization to dramatically enhance fat-soluble nutrient absorption. These technologies can increase bioavailability by 300-500%[20].
The Mitochondrial Support Liquid vs. Capsule Comparison
| Factor | Liquid Shots | Standard Capsules |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption Speed | 15-30 minutes, begins in mouth and esophagus | 45-90 minutes, requires full digestion process |
| Bioavailability | 40-90% depending on formulation technology | 5-15% for fat-soluble nutrients like CoQ10 |
| Digestive Ease | Minimal digestive burden, suitable for sensitive systems | Requires robust digestive function, may cause upset |
| Mitochondrial Uptake | Rapid cellular delivery in bioavailable forms | Delayed and reduced cellular availability |
| Dosage Flexibility | Easily adjustable, precise dosing possible | Fixed doses, difficult to customize |
| Effectiveness Timeline | Noticeable effects within days to 1 week | May require 2-4 weeks for noticeable effects |
Clinical Evidence for Liquid Superiority
A comparative study of liquid CoQ10 versus standard powder-
References
NCBI: Coenzyme Q10 and its Essential Role in Mitochondrial ATP Production
MDPI Nutrients: Comparative Bioavailability of Liquid vs. Solid Vitamin Formulations
Frontiers in Physiology: Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and the Impact of B-Vitamin Co-factors
Linus Pauling Institute: Absorption and Efficacy of Oral Liquid Micronutrients
Mayo Clinic: Clinical Overview of Nutrients for Cellular Energy and Fatigue Reduction
Journal of Clinical Medicine: The Role of B-Complex in Mitochondrial Biogenesis
National Institute of Health (NIH): Vitamin B12 Fact Sheet for Health Professionals on Energy Metabolism
Harvard Health: The Importance of Mitochondrial Health in Aging and Vitality
Journal of Cell Biology: Mechanisms of ATP Synthesis and Mitochondrial Respiration
Nutritional Reviews: Liquid Delivery Systems for Enhanced Nutrient Bioaccessibility
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology: Mitochondrial Quality Control and Cellular Energy Homeostasis
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition: Oral Bioavailability of Antioxidants like Glutathione and CoQ10
Scientific Reports: NAD+ Metabolism and its Role in Mitochondrial Health and Longevity
Endocrinology & Metabolism: The Krebs Cycle: How Micronutrients Fuel the Mitochondrial Engine
Journal of Nutrition & Metabolism
Cochrane Library: Review of Oral Vitamin Supplementation for Reducing Fatigue Symptoms
Cell Metabolism Journal: Nutrient Sensing and Mitochondrial Adaptation to Metabolic Stress
Cleveland Clinic: Understanding Cellular Energy and the Role of Mitochondria in Health
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: Bioavailability of Vitamin B12 in Liquid Formulations vs. Tablets
Aging Cell: Nutritional Interventions to Improve Mitochondrial Function in Humans


.png)
